Electrolyte Tolerance in Formulations: Why It Matters & How to Choose the Right Modifier
When it comes to cosmetic formulations, texture, stability, and performance are all determined by one critical factor—rheology. Whether you’re developing a high-clarity serum, a rich moisturizer, or a silky cleanser, the right rheology modifier ensures that the final product spreads well, stays stable, and delivers an optimal sensory experience.
But what happens when electrolytes—such as actives, surfactants, and preservatives—enter the mix? These charged molecules can interfere with thickening systems, leading to viscosity loss, phase separation, or unexpected texture changes. If you’ve ever formulated a product that suddenly thinned out after adding an active, electrolytes were likely the culprit.
So, how can formulators prevent electrolyte-induced viscosity breakdown? The key lies in choosing the right rheology modifier—one that can withstand electrolytes without compromising stability.
How Electrolytes Impact Viscosity & Stability
Electrolytes are charged particles (salts, acids, or bases) that can dramatically alter the behavior of rheology modifiers. They’re present in a wide range of cosmetic ingredients, including:
- Active Ingredients – Sodium PCA, Magnesium Ascorbyl Phosphate, Niacinamide.
- Surfactants & Cleansers – Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Sodium Cocoyl Isethionate.
- Preservatives – Sodium Benzoate, Potassium Sorbate.
- pH Adjusters – Citric Acid, Sodium Hydroxide.
While these ingredients enhance performance and stability in many formulations, they can also disrupt traditional thickening systems.
What Happens When Electrolytes Interact with Thickeners?
- Standard carbomers, which rely on an electrostatic repulsion mechanism to build viscosity, often experience thickening failure when electrolytes are present.
- Hydrophobically modified crosspolymers (such as AQUPEC® crosspolymers) are more electrolyte-tolerant due to their unique polymer structure.
- Some specialized thickeners, like AQUPEC® SER W-300C, actually require electrolytes to build viscosity, making them ideal for high-electrolyte formulations.
The challenge for formulators is finding a rheology modifier that can handle electrolytes while still providing good viscosity, clarity, and sensory properties.
Choosing the Right Rheology Modifier for Electrolyte-Rich Formulas
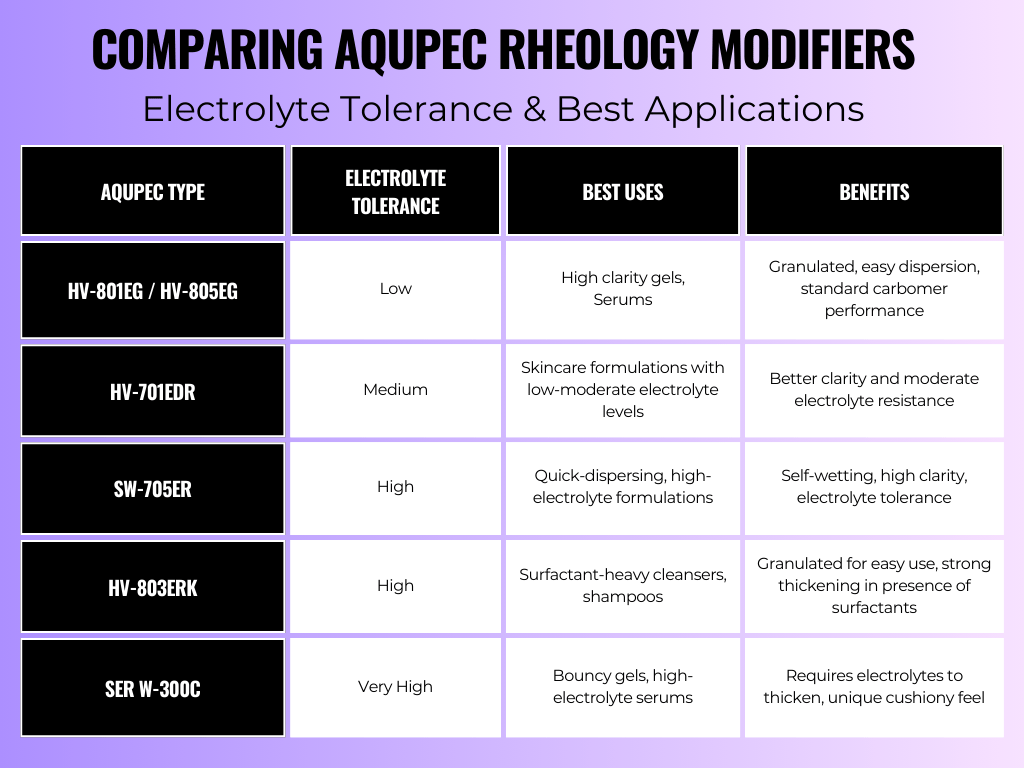
To formulate effectively in electrolyte-heavy environments, it’s essential to select the right type of thickener. Below is a breakdown of AQUPEC® Carbomers vs. Crosspolymers, highlighting their electrolyte tolerance and ideal applications.

Formulation Checklist: How to Choose the Right AQUPEC Modifier
Before selecting a rheology modifier, ask yourself:
- What is the electrolyte content of my formula?
- How quickly do I need it to disperse?
- What texture am I trying to achieve?
- For bouncy, cushiony textures → Use SER W-300C.
- For soft-focus and light feel → Use MG N40R.
- For high clarity → Use HV-701EDR or SW-705ER.
- Does my thickener need to be pre-neutralized?
- If yes, MG N40R saves time and eliminates neutralization steps.
- If not, standard carbomers require adjusting pH for thickening.
Final Thoughts: Optimizing Electrolyte-Resistant Formulations
When working with electrolyte-rich cosmetic formulations, selecting the right rheology modifier is essential for maintaining viscosity, clarity, and performance.
- For low-electrolyte systems, traditional carbomers (HV series) work well.
- For moderate electrolyte resistance, HV-701EDR offers better clarity.
- For high electrolyte resistance, SW-705ER and HV-803ERK are best.
- For extreme electrolyte tolerance, SER W-300C is the best choice.
By choosing the right AQUPEC modifier, formulators can prevent viscosity loss, enhance stability, and create luxurious, high-performance products.
Need help selecting the best rheology modifier for your next project? Contact us today to explore the AQUPEC collection and find the perfect fit!



